How To Draw A Box Plot Deleting Outliers In R
Remove Outliers from Data Set up in R (Instance)
In this article you'll learn how to delete outlier values from a information vector in the R programming language.
Table of contents:
Allow's swoop into information technology.
Creation of Example Data
Accept a look at the following instance data:
gear up . seed ( 937573 ) # Create randomly distributed data ten <- rnorm( thou ) x[ one : 5 ] <- c( 7, ten, - five, 16, - 23 ) # Insert outliers 10 # Print information # [1] 7.000000000 x.000000000 -5.000000000 16.000000000 -23.000000000 -0.413450746 0.801720348 ...
set.seed(937573) # Create randomly distributed data x <- rnorm(1000) x[ane:five] <- c(7, ten, - 5, sixteen, - 23) # Insert outliers x # Print information # [i] 7.000000000 10.000000000 -v.000000000 xvi.000000000 -23.000000000 -0.413450746 0.801720348 ...
The previous output of the RStudio console shows the construction of our example data – It'due south a numeric vector consisting of 1000 values.
Now, we can draw our data in a boxplot every bit shown beneath:
boxplot(x) # Create boxplot of all information
boxplot(x) # Create boxplot of all data
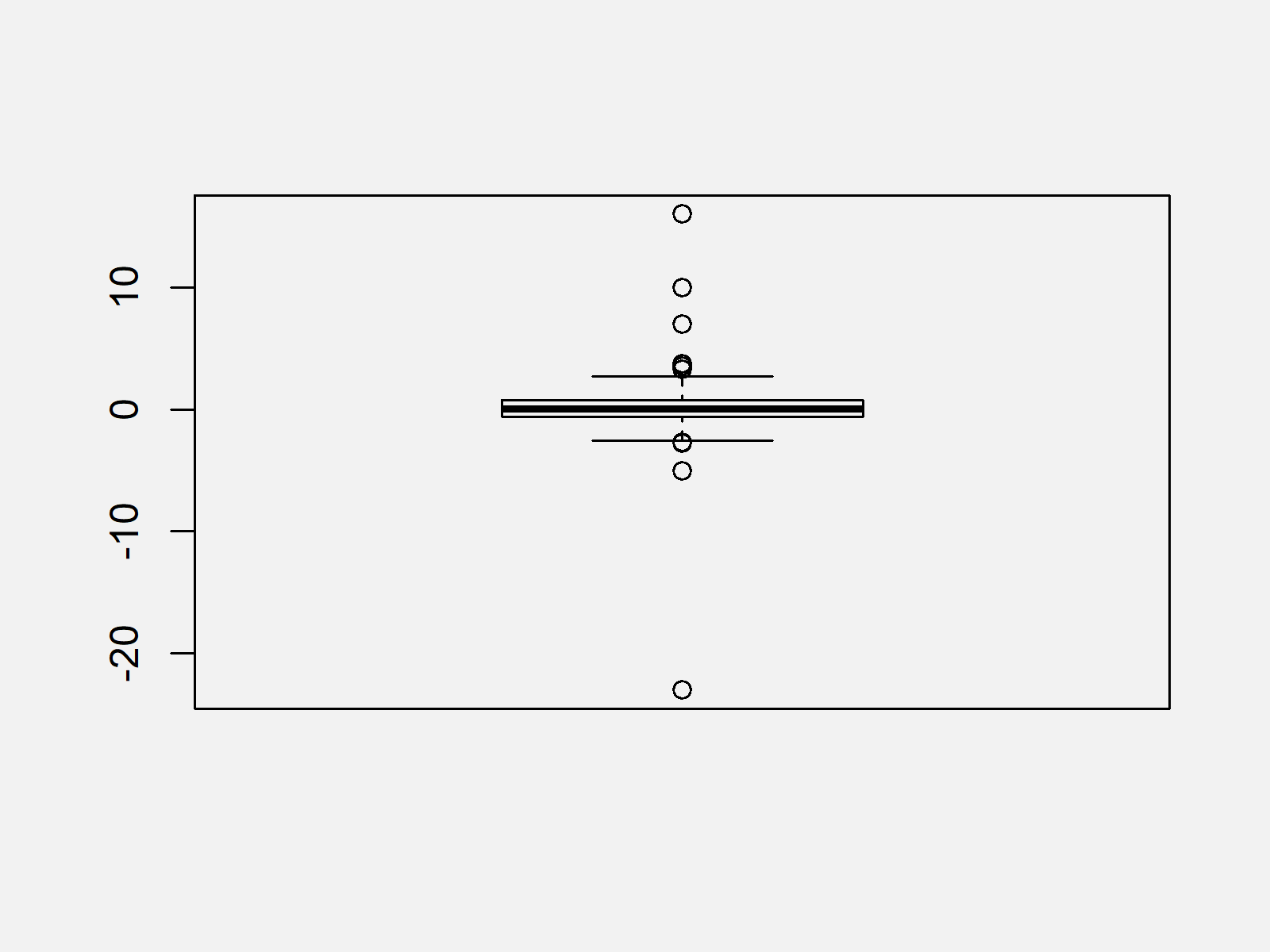
As shown in Figure 1, the previous R programming syntax created a boxplot with outliers.
Example: Removing Outliers Using boxplot.stats() Function in R
In this Department, I'll illustrate how to identify and delete outliers using the boxplot.stats function in R. The post-obit R code creates a new vector without outliers:
x_out_rm <- x[ !ten %in% boxplot. stats (x)$out] # Remove outliers
x_out_rm <- x[!ten %in% boxplot.stats(x)$out] # Remove outliers
Permit'due south check how many values we have removed:
length(x) - length(x_out_rm) # Count removed observations # 10
length(ten) - length(x_out_rm) # Count removed observations # 10
We have removed x values from our data. Note that we have inserted simply five outliers in the data creation process above. In other words: We deleted five values that are no real outliers (more about that beneath).
However, now nosotros tin draw some other boxplot without outliers:
boxplot(x_out_rm) # Create boxplot without outliers
boxplot(x_out_rm) # Create boxplot without outliers
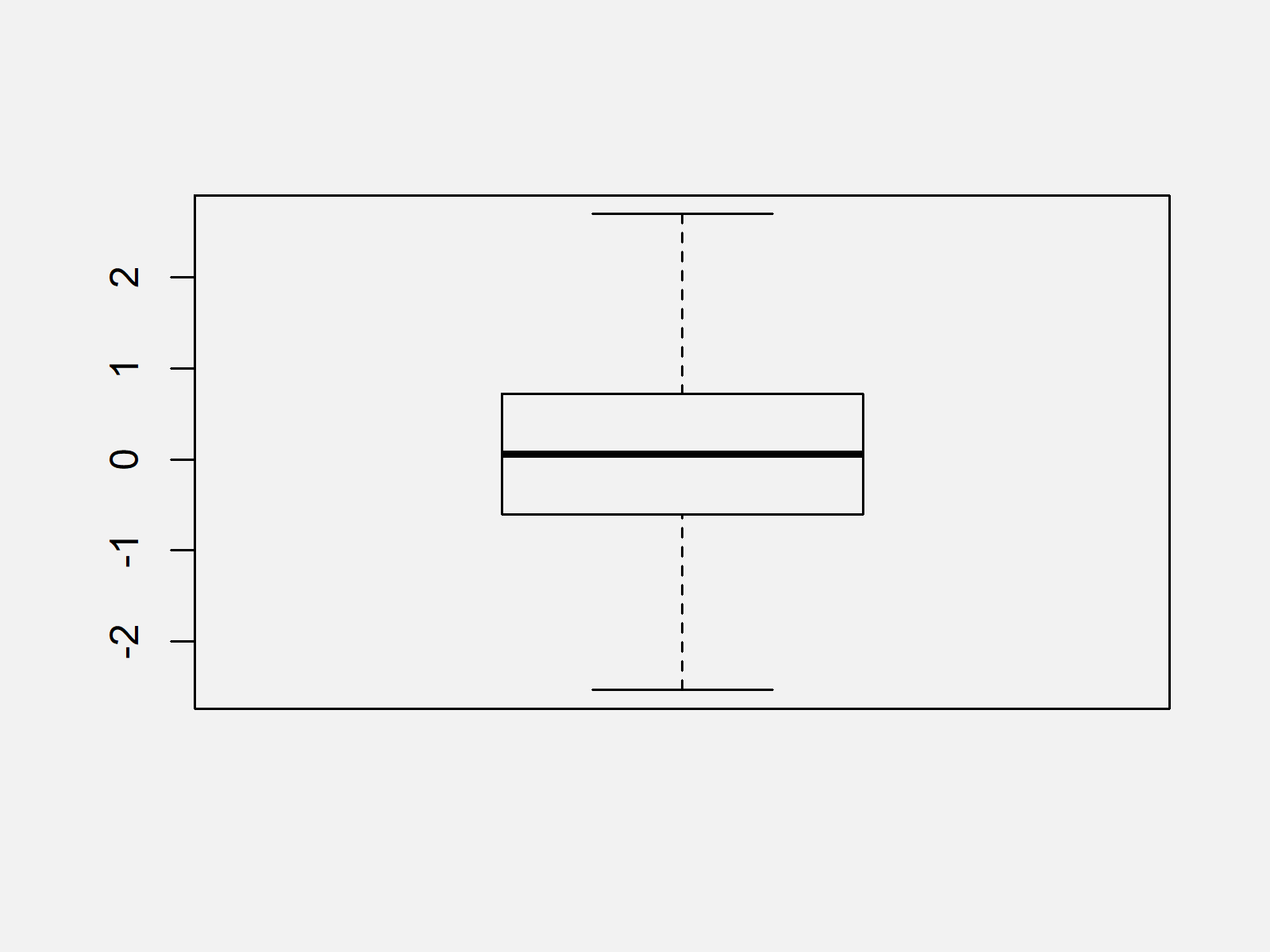
The output of the previous R lawmaking is shown in Effigy 2 – A boxplot that ignores outliers.
Of import note: Outlier deletion is a very controversial topic in statistics theory. Whatsoever removal of outliers might delete valid values, which might lead to bias in the analysis of a data set.
Furthermore, I have shown you a very simple technique for the detection of outliers in R using the boxplot function (accept a look at the documentation of boxplots.stats for more than details). However, in that location be much more advanced techniques such as machine learning based anomaly detection.
I strongly recommend having a expect at the outlier detection literature (e.g. this commodity) to make sure that you lot are not removing the wrong values from your information set.
Video, Further Resources & Summary
I have recently published a video on my YouTube channel, which explains the topics of this tutorial. You can find the video below.
Furthermore, you may read the related tutorials on this website.
- Remove Duplicated Rows from Information Frame in R
- Ignore Outliers in ggplot2 Boxplot in R
- Create a Box-and-Whisker Plot
- R Programming Examples
This tutorial showed how to detect and remove outliers in the R programming language. Please let me know in the comments below, in case you have additional questions.
Source: https://statisticsglobe.com/remove-outliers-from-data-set-in-r
Posted by: paigewilier88.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Draw A Box Plot Deleting Outliers In R"
Post a Comment